1. Calcium (Ca) is abundant in soils of the upper Midwest, northern Great Plains, and Canadian Prairies; calcium deficiency in agronomic crops is rare
Calcium makes up about 3.6% of the Earth’s crust, and it is relatively abundant in agricultural soils across the region. In soils with pH greater than 6.0, Ca is the dominant cation (positively charged ion) on the cation exchange capacity (CEC). Since most soils in the region have a pH of 6.0 or above, calcium is very abundant and soils with low soil test Ca (less than 500 ppm) are rare (Figure 1).
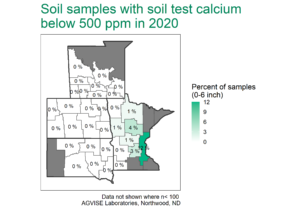
Figure 1. AGVISE regional soil test summary. AGVISE has created regional summaries for the past 40 years. You can find more soil test summary data, including Montana and Canada, here.
Potential calcium deficiencies are most common on sandy soils with strongly acidic pH (pH less than 5.0). Luckily, the fix for low soil pH also fixes potential Ca deficiencies. To correct soil pH, agricultural limestone is applied to raise soil pH to 6.0 or 6.5, if growing sensitive crops like alfalfa or clover. When limestone (calcium carbonate) is applied in tons per acre, more than enough calcium is also applied and sufficiently increases soil test Ca, providing ample calcium for optimal crop growth and development. Throughout the region, soils with low soil pH are more common in the higher rainfall areas to the east and south (Figure 2), and liming is a standard practice to correct soil pH and provide calcium.
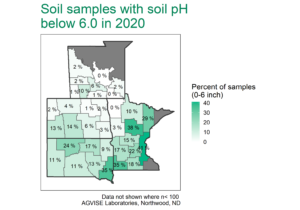
Figure 2. Soil samples with pH below 6.0 in 2020, where lime application may be required. The number of fields with low pH has increased over time and will continue to do so because soil acidification is a natural process. Keep watch for low soil pH, especially in western North Dakota and South Dakota. You can find more soil test summary data, including Montana and Canada, here.
2. Multiple calcium fertilizer sources exist; some increase pH, others do not
Agricultural limestone is the most common lime source and is available in two flavors: calcitic (calcium carbonate, <5% magnesium) or dolomitic (calcium-magnesium carbonate, >5% magnesium). Limestone quarries exist in southern Minnesota and Iowa, but the northern Great Plains is virtually devoid of mineable limestone. Industrial waste lime (spent lime) is another good lime source and available from sugar beet processing plants and water treatment plants throughout the region. Any of these liming materials will supply enough calcium to increase soil test Ca if soil pH is increased above pH 6.0.
Gypsum (calcium sulfate) is another calcium source, but it does not change soil pH. Gypsum is sometimes used to increase soil test Ca if the producer does not want to increase soil pH with lime application. This situation is common in irrigated potato production where increased soil pH may increase soil-borne diseases like common scab of potato. Gypsum is not a lime source, so it will not increase soil pH.
3. There is no “ideal” base cation saturation range or ratio for calcium
Suggestions that Ca and other base cations (magnesium, potassium) are required in a certain percentage or ratio in soil are not supported by modern science. Recent research done at several universities shows a wide range of base cation ratios in soil will support normal crop growth (see links below). What is important is that a sufficient soil test amount of each base cation (Ca Mg, K) is present in soil to support plant growth and development.
4. Soils with pH greater than 7.3 will have falsely inflated soil test Ca and cation exchange capacity (CEC) results
Soils with pH greater than 7.3 will contain some amount of naturally occurring calcium carbonate (CaCO3), shown on the soil test report as carbonate (CCE). The calcium soil test method will extract Ca on cation exchange sites and some Ca from calcium carbonate minerals, resulting in an inflated soil test Ca result. Starting with inflated soil test Ca, the routine cation exchange capacity (CEC) calculation is also inflated. For example, a soil with pH 7.8 and 3.0% CCE may report CEC at 60 meq/100 g, but the correct CEC is only 27 meq/100 g. To obtain accurate CEC results on soil with pH greater than 7.3, a special displacement CEC laboratory method is required. For soils with pH less than 7.3, the routine CEC calculation method will provide accurate soil test Ca and CEC results. High soil salinity (soluble salts, EC) can also inflate CEC results.
5. Calcium is not an environmental risk to surface or ground water
Calcium is one of the major dissolved substances found in surface and ground waters, especially in the northern Great Plains and Canadian Prairies. In fact, water hardness is determined from the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in water. There is already so much calcium found in natural waters in the region that calcium fertilizer additions to soil are negligible. Water hardness does affect the effectiveness of some herbicides and may cause tank-mixing issues, but is not an environmental concern.
Bonus: Just because your tomatoes have had blossom-end rot does NOT mean your soil is Ca deficient!
If you are a backyard tomato grower, you may have experienced blossom-end rot before, where the blossom-end of developing fruits turn brown and mushy while still on the plant. Yes, the problem is caused by low calcium in the tomato plant, but not necessarily because the soil has low soil test Ca. Blossom-end rot is primarily caused by inconsistent soil moisture. Adequate soil moisture is required to maintain a consistent supply of calcium moving to the plant root, which might run short if watering is inconsistent. To keep blossom-end rot away from your garden, just try to be more consistent with watering, especially during dry periods.
Resources on Base Cation Saturation Ratios
Cation Exchange: A Review, IPNI
Soil Cation Ratios for Crop Production, UMN
A Review of the Use of the Basic Cation Saturation Ratio and the “Ideal” Soil, SSSA Journal

AGVISE Laboratories: Trusted by University and Industry Researchers
in Plant Analysis, Research, Soil Analysis/by John LeeWhile you may know AGVISE Laboratories for the soil and plant analysis services we provide you and your producers, AGVISE also has a long history of supporting university and industry research. For the past 30 years, many university-operated soil testing laboratories have closed in the region. This has left a gap in the on- and off-campus research capacities at some institutions. To help bridge the gap, AGVISE partners with university and industry researchers to provide the laboratory analysis services they need to further research in soil fertility, plant nutrition, nutrient use efficiency, and many other areas. Researchers choose AGVISE for their research projects because of our reliability, consistence, and standard of excellence.
Each year, AGVISE analyzes thousands of soil and plant samples for researchers across the United States and Canada. You may have even heard of some recent research projects for which we provided the analysis services. A unique collaborative project was the Public–Industry Partnership for Enhancing Corn Nitrogen Research, which included eight land-grant universities and USDA-ARS. AGVISE analyzed thousands of soil and plant samples for researchers from the University of Illinois, Purdue University (Indiana), Iowa State University, University of Minnesota, University of Missouri, University of Nebraska, North Dakota State University, and University of Wisconsin. We are proud of our small part in support of this research that provided critical information to corn producers and helping them improve nitrogen management. You can read more about the project in the links below.
Another research project that AGVISE is helping with is the Potato Soil Health Project, supported by USDA-NIFA Specialty Crop Research Initiative (SCRI) and spearheaded by the potato industry. The research project includes eight potato-growing states across a range of diverse soils. In addition to soil fertility analysis, AGVISE is also helping evaluate soil health using biological activity (24-h CO2 respiration), active carbon (POXC), bioavailable nitrogen (ACE), and soil aggregate stability. AGVISE Laboratories is a strong supporter of soil health research, and we are excited to have been chosen to provide soil health analyses for the research project.
In addition to these large research projects, AGVISE also provides analysis services for many research organizations and universities throughout the region, including Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, University of Manitoba, Montana State University, University of Saskatchewan, and South Dakota State University.
The next time you send your soil or plant samples to AGVISE Laboratories, you can be confident that you will be receiving the highest quality analyses and service, just like we provide to researchers across the United States and Canada.
Some open-access articles from AGVISE-supported university research projects
A Public-Industry Partnership for Enhancing Corn Nitrogen Research and Datasets: Project Description, Methodology, and Outcomes
When to Use a Single or Split Application of Nitrogen Fertilizer in Corn
Which Recommendation Tools Are Best for Achieving the Economically Optimal Nitrogen Rate?
The Potato Soil Health Project funded through USDA-NIFA SCRI
5 Things You Should Know About Phosphorus
in Phosphorus, Regional Data, Soil Chemical Analysis/by John Lee1. The two accepted soil phosphorus tests in the North Central Region are the Olsen and Bray-P1 methods
The Olsen (bicarbonate) method is the standard soil P test in the North Central region. This method was developed to work on soils with low and high pH. The Olsen method works well in precision soil sampling, where the same field may have zones with acidic and calcareous soils. The Bray P-1 method is another accepted method in our region, but not always recommended. This method was developed in the U.S. Corn Belt, has a long history of soil test calibration studies and works well on acidic soils. The Bray P-1 method fails on soils with pH greater than 7, producing results with false low soil test P. Therefore, it has remained limited to the U.S. Corn Belt proper. The Mehlich-3 method was introduced as a multi-nutrient soil extractant. But like the Bray P-1 method, the acidic Mehlich-3 method does not perform well on calcareous soils; therefore, it has not gained approval by universities in the northern Great Plains and Canadian Prairies.
All soil P test methods are designed to predict the probability of crop response to P fertilization. The methods measure the plant-available P pool. Since the soil test method is an index of availability, the units are reported in parts per million (ppm) and ranked low, medium, or high based on university soil test calibration research. No soil P test method measures the actual pounds of available P in soil, they are only indexes of crop response.
2. Most soils in the Northern Plains/Canadian Prairies region could use more phosphorus
Soils in the region are naturally low in P and historical P fertilizer use has been low, relative to crop P removal. As a result, many areas in the region still have low soil test P (below soil test critical level of 15 ppm Olsen P) after many decades of crop production. In other words, most farmers are not over-applying P. In fact, soils with low soil test P should receive moderate to high rates of fertilizer P each year to achieve good crop yield and maximize profitability.
Figure 1. Map developed using AGVISE soil test data. AGVISE has created regional summaries like this for the past 40 years. Check out the summary data for Montana and Canada and summaries of other nutrients and soil properties here.
3. You should use starter phosphorus fertilizer
Starter fertilizer placed near, or with the seed, is critical for crops like corn and wheat, regardless of soil test P level. A P fertilizer band placed near the seed will ensure soluble P near developing plant roots and results in vigorous early season growth, which is important in cold, wet soil conditions. Placing P fertilizer in bands also improves P use efficiency, especially in soils with relatively low or high pH. Phosphorus availability is greatest near soil pH 6.5. Since changing soil pH is difficult and costly, fertilizer P use efficiency is more easily improved with application in fertilizer bands to reduce the volume of soil involved in P fixation reactions.
4. Phosphorus source doesn’t really matter
No matter the starting material, all P fertilizers go through the same chemical reactions in the soil. It does not matter if the fertilizer starts as a poly-phosphate or ortho-phosphate. Within about one week in the soil, all P fertilizer sources react to form lower solubility compounds. What is more important than source is the placement of the fertilizer to increase availability (banding) and the rate of actual P fertilizer applied.
5. Phosphorus can be an environmental concern
Phosphorus entering surface waters can create algae blooms and fish kills. Since P is not mobile in soil, the P leaching risk is very low. However, P does move to surface waters with soil particles when erosion occurs. In cold climates like those on the northern Great Plains and Canadian Prairies, dissolved P released from vegetation can move with snow melt to surface water.
For more information about phosphorus and its reactions in soil, explore the links below:
Understanding Phosphorus in Minnesota Soils (Univ. Minnesota)
Understanding Plant Nutrients: Soil and Applied Phosphorus (Univ. Wisconsin)
Phosphorus Facts: Soil, plant, and fertilizer (Kansas State Univ.)
5 Things You Should Know About Calcium
in Base Cation Saturation Ratio, Calcium, Regional Data, Soil Chemical Analysis, Soil pH/by John Lee1. Calcium (Ca) is abundant in soils of the upper Midwest, northern Great Plains, and Canadian Prairies; calcium deficiency in agronomic crops is rare
Calcium makes up about 3.6% of the Earth’s crust, and it is relatively abundant in agricultural soils across the region. In soils with pH greater than 6.0, Ca is the dominant cation (positively charged ion) on the cation exchange capacity (CEC). Since most soils in the region have a pH of 6.0 or above, calcium is very abundant and soils with low soil test Ca (less than 500 ppm) are rare (Figure 1).
Figure 1. AGVISE regional soil test summary. AGVISE has created regional summaries for the past 40 years. You can find more soil test summary data, including Montana and Canada, here.
Potential calcium deficiencies are most common on sandy soils with strongly acidic pH (pH less than 5.0). Luckily, the fix for low soil pH also fixes potential Ca deficiencies. To correct soil pH, agricultural limestone is applied to raise soil pH to 6.0 or 6.5, if growing sensitive crops like alfalfa or clover. When limestone (calcium carbonate) is applied in tons per acre, more than enough calcium is also applied and sufficiently increases soil test Ca, providing ample calcium for optimal crop growth and development. Throughout the region, soils with low soil pH are more common in the higher rainfall areas to the east and south (Figure 2), and liming is a standard practice to correct soil pH and provide calcium.
Figure 2. Soil samples with pH below 6.0 in 2020, where lime application may be required. The number of fields with low pH has increased over time and will continue to do so because soil acidification is a natural process. Keep watch for low soil pH, especially in western North Dakota and South Dakota. You can find more soil test summary data, including Montana and Canada, here.
2. Multiple calcium fertilizer sources exist; some increase pH, others do not
Agricultural limestone is the most common lime source and is available in two flavors: calcitic (calcium carbonate, <5% magnesium) or dolomitic (calcium-magnesium carbonate, >5% magnesium). Limestone quarries exist in southern Minnesota and Iowa, but the northern Great Plains is virtually devoid of mineable limestone. Industrial waste lime (spent lime) is another good lime source and available from sugar beet processing plants and water treatment plants throughout the region. Any of these liming materials will supply enough calcium to increase soil test Ca if soil pH is increased above pH 6.0.
Gypsum (calcium sulfate) is another calcium source, but it does not change soil pH. Gypsum is sometimes used to increase soil test Ca if the producer does not want to increase soil pH with lime application. This situation is common in irrigated potato production where increased soil pH may increase soil-borne diseases like common scab of potato. Gypsum is not a lime source, so it will not increase soil pH.
3. There is no “ideal” base cation saturation range or ratio for calcium
Suggestions that Ca and other base cations (magnesium, potassium) are required in a certain percentage or ratio in soil are not supported by modern science. Recent research done at several universities shows a wide range of base cation ratios in soil will support normal crop growth (see links below). What is important is that a sufficient soil test amount of each base cation (Ca Mg, K) is present in soil to support plant growth and development.
4. Soils with pH greater than 7.3 will have falsely inflated soil test Ca and cation exchange capacity (CEC) results
Soils with pH greater than 7.3 will contain some amount of naturally occurring calcium carbonate (CaCO3), shown on the soil test report as carbonate (CCE). The calcium soil test method will extract Ca on cation exchange sites and some Ca from calcium carbonate minerals, resulting in an inflated soil test Ca result. Starting with inflated soil test Ca, the routine cation exchange capacity (CEC) calculation is also inflated. For example, a soil with pH 7.8 and 3.0% CCE may report CEC at 60 meq/100 g, but the correct CEC is only 27 meq/100 g. To obtain accurate CEC results on soil with pH greater than 7.3, a special displacement CEC laboratory method is required. For soils with pH less than 7.3, the routine CEC calculation method will provide accurate soil test Ca and CEC results. High soil salinity (soluble salts, EC) can also inflate CEC results.
5. Calcium is not an environmental risk to surface or ground water
Calcium is one of the major dissolved substances found in surface and ground waters, especially in the northern Great Plains and Canadian Prairies. In fact, water hardness is determined from the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in water. There is already so much calcium found in natural waters in the region that calcium fertilizer additions to soil are negligible. Water hardness does affect the effectiveness of some herbicides and may cause tank-mixing issues, but is not an environmental concern.
Bonus: Just because your tomatoes have had blossom-end rot does NOT mean your soil is Ca deficient!
If you are a backyard tomato grower, you may have experienced blossom-end rot before, where the blossom-end of developing fruits turn brown and mushy while still on the plant. Yes, the problem is caused by low calcium in the tomato plant, but not necessarily because the soil has low soil test Ca. Blossom-end rot is primarily caused by inconsistent soil moisture. Adequate soil moisture is required to maintain a consistent supply of calcium moving to the plant root, which might run short if watering is inconsistent. To keep blossom-end rot away from your garden, just try to be more consistent with watering, especially during dry periods.
Resources on Base Cation Saturation Ratios
Cation Exchange: A Review, IPNI
Soil Cation Ratios for Crop Production, UMN
A Review of the Use of the Basic Cation Saturation Ratio and the “Ideal” Soil, SSSA Journal
Soybean Iron Deficiency Chlorosis: Symptoms, Causes, and Management
in Iron, Soybean/by John BrekerFigure 1. Soybean plants with iron deficiency chlorosis symptoms. Note the newest leaves are yellow with indistinct green veins.
If soybean turns yellow during an early growth stage, you may have a case of soybean iron deficiency chlorosis (IDC). The distinctive yellow symptoms of soybean IDC often appear as soybean enters the first- to third-trifoliate leaf stage. Soybean IDC is characterized by distinct interveinal chlorosis (yellow leaf with green leaf veins) in the newest leaves and may result in substantial yield loss (Figure 1). Soybean IDC is not caused by low soil iron but instead caused by soil conditions that decrease iron uptake by soybean roots.
Soybean IDC risk and severity are primarily related to soil carbonate content (calcium carbonate equivalent, CCE) and worsened by salinity (electrical conductivity, EC) (Table 1). Soybean IDC is common in soybean-growing regions of the upper Midwest, northern Great Plains, and Canadian Prairies, where soils frequently have high carbonate and/or salinity (Figure 2). Within a field, IDC symptoms are usually confined to soybean IDC hotspots with high carbonate and salinity; however, symptoms may appear across a field if high carbonate and salinity are present throughout the field. Soybean IDC severity is made worse in cool, wet soils and soils with high residual nitrate-nitrogen. Soil pH is not a good indicator of soybean IDC risk because some high pH soils lack high carbonate and salinity, which are the two principal risk factors.
Figure 2. Soil samples with high risk of soybean iron deficiency chlorosis (IDC) in the northern Great Plains and upper Midwest.
Unlike a nitrogen or sulfur deficiency, soybean IDC is not correctable with an in-season fertilizer application. Foliar application of iron fertilizers, including FeEDDHA, may have short-term cosmetic effects, but foliar iron applications have not consistently increased soybean yield on IDC-affected plants. Chlorosis symptoms often alleviate naturally as environmental conditions improve (e.g. drier, warmer weather), but severe cases can persist and cause yield loss. North Dakota State University research has shown that IDC persisting into the fifth- and sixth-trifoliate leaf stage will significantly reduce soybean yield. For fields with historical soybean IDC problems, you should delineate soybean IDC hotspots for selective management using aerial or satellite imagery.
Guidelines for managing soybean IDC
Figure 3. Soybean iron deficiency chlorosis (IDC) severity is reduced with iron fertilization. However, IDC-tolerant soybean varieties are more effective. Research from Dr. R. Jay Goos, NDSU, 2000.
Fallow Syndrome: Preventing Phosphorus Problems
in Canola, Cover Crop, Phosphorus, Prevented Planting, Soil Health, Starter Fertilizer, Sugar Beet/by Jodi BoeSome crops that do not support mycorrhizal fungi (left to right: sugar beet, canola, radish).
Producers in the northern Great Plains and upper Midwest need to consider the risk of fallow syndrome in their crop nutrition plans. You are probably asking, what is “fallow syndrome” and why should I care? After all, summer fallow is not that common anymore! But the greater number of Prevented Planting acres in 2019 and 2020 meant that we have had many unintended fallow fields, making fallow syndrome a serious and widespread concern for the next year.
Fallow syndrome is an induced phosphorus deficiency caused by a lack of mycorrhizal fungi in soil. Some plant species, like corn and wheat, rely heavily on mycorrhizae to colonize the plant root system and help acquire important nutrients like phosphorus and zinc. If soil is lacking sufficient mycorrhizae to colonize plant roots, a case of fallow syndrome will increase phosphorus fertilizer needs and even cost crop yield potential.
Understanding mycorrhizae
Mycorrhizae fungi occur naturally in soils and readily colonize plant roots. Upon root colonization, mycorrhizae fungal filaments act as extensions of the root system and increase the soil volume available for plant water and nutrient uptake. The combined root-mycorrhizae surface area can be up to 10-fold greater than roots without mycorrhizae. Mycorrhizae depend on living plant roots to support stable mycorrhizae populations. However, not all plant species host and support mycorrhizae growth. Some common field crops are non-host species and their planting results in rapid drops in mycorrhizae populations.
Summer fallow or unplanted cropland, such as Prevented Planting in 2020, is a classic example of providing no or few living plant roots in soil to maintain mycorrhizae populations. In addition, some crop species do not support mycorrhizae, such as those in the goosefoot family (sugar beet) and mustard family (canola, radish, turnip). Following a classic case of summer fallow or a non-mycorrhizae supporting crop, the mycorrhizae population in soil will quickly drop. A cover crop mix that included a grass species (e.g. barley, rye) should still support mycorrhizae and prevent fallow syndrome concerns.
Preventing fallow syndrome
The easiest prevention strategy after fallow is planting a crop species without fallow syndrome risk like soybean, canola, or sugar beet. Avoid planting susceptible crops like corn and wheat. These crops are highly dependent on mycorrhizae to acquire phosphorus, and extra starter phosphorus will be required if fallow syndrome risk is present.
To reduce fallow syndrome risk in corn or wheat, extra phosphorus fertilizer must be placed with or near the seed. Applying more broadcast phosphorus or relying on high soil test P will not prevent fallow syndrome. The starter phosphorus rate should be 20 to 40 lb/acre P2O5. In some university research trials, up to 60 lb/acre P2O5 with 2×2-band placement near the seed was needed to prevent corn yield loss to fallow syndrome.
For wheat, these phosphorus rates are typically seed safe with monoammonium phosphate (MAP, 11-52-0). Most corn planters can safely apply 20 lb/acre P2O5 (5 gal/acre ammonium polyphosphate, APP, 10-34-0) in the furrow. For medium/fine-textured soils with good soil moisture at planting, you can generally apply up to 10 gal/acre 10-34-0 (40 lb/acre P2O5) safely in the furrow at 30-inch row spacing. Higher 10-34-0 rates may exceed seed safety limits on dry soils or coarse-textured soils and require 2×2-band placement to maintain seed safety.
Complete liquid fertilizers, such as 6-24-6 or 9-18-9, are not suggested for preventing fallow syndrome. Compared to 10-34-0, the products have lower P concentration that result in less applied phosphorus, even if used at maximum seed safe rates. The extra N + K2O in “complete” liquid fertilizers increases the salt index and lowers the seed safe rate.
Field Variability Screaming in Your Ear? Precision Soil Sampling is the Answer
in Precision Ag/by Jodi BoeYour land is variable. Each fall, you watch the combine yield monitor go up and down across the field. You know where crop yield will be the best in wet years and dry years. So, why do you still use a whole-field composite soil test to manage fertilizer inputs and ignore the obvious field variability affecting crop yield potential?
Precision soil sampling, using grids or zones, divides whole fields into smaller units for soil sampling and creates more accurate and useful soil test information. It tells you exactly where you need to apply more or less fertilizer within each field, unlocking untapped crop yield potential and fertilizer input savings. Grid soil sampling, which is the most detailed approach, typically breaks a field into 2.5- to 5.0-acre grid cells. The more adaptable approach is zone soil sampling, which divides the field into productivity zones that can be managed to their needs. A well-designed zone should represent the smallest practical management unit that still accurately represents the area (e.g. 20-40 acres). Zones are commonly created using data layers such as crop yield, satellite imagery, soil survey, topography, salinity, drainage, or a combination of several data layers.
Precision soil test data can reveal previously unknown production problems, which were otherwise masked in a whole-field composite soil sample. For example, more zone soil sampling has uncovered more and more low soil pH zones (below pH 6) in the long-term no-till areas of central South Dakota, southwest North Dakota, and north-central Montana. Previously, the whole-field composite soil sample had blended the low and high soil pH zones together and everything looked okay. But now, the zone soil samples are revealing where low soil pH is causing serious crop yield loss and where soil pH can be corrected with lime to improve crop yield. This is a good example of precision soil sampling revealing a long-hidden problem and showing us how to fix it.
If you break a field into smaller and smaller units (i.e. more zones), you will learn more and more about field variability. To illustrate the concept, we pulled soil test data from 23,000 zone sampled fields in 2020 and calculated the average soil test range (difference) between the high and low zones within each field. The summarized data is presented in the table.
lb/acre, 0-24 inch
ppm
ppm
%
As the number of zones increases in a field, the range in soil test values (high zone – low zone) also increases and highlights the true variability across the field. The trend is clear not just for soil nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, but also for soil properties like pH and organic matter. This tells us that one whole-field “average,” was missing the highs and lows that occur naturally in many fields.
Precision soil sampling is the first step in understanding what is really happening in your fields. You can gain a clearer picture of what plant nutrient deficiencies might be occurring and where you can improve crop yield potential. The next step is creating variable-rate prescriptions for seed, fertilizer, lime, and even herbicides (consider soil pH and organic matter). These tools can help you improve crop yield, optimize crop inputs, and increase profitability within each field on your farm.
Prevented Planting Acres in 2020: Maximizing Cover Crop Effectiveness
in Cover Crop, Prevented Planting, Soil Erosion, Soil Health, Tillage, Water Quality, Weed/by John BrekerIn 2020, there are again widespread acres of Prevented Planting (PP) in North Dakota and northwest Minnesota. Farmers are now making plans to plant cover crops on unplanted cropland in the next few weeks. It is important to establish cover crops on PP fields because growing plants help reduce the chance these fields will be PP fields again next year.
Let’s look at the major reasons why cover crops are valuable tools on Prevented Planting acres.
Soil Water Use
A field without any growing plants is a fallow field. Before no-till, summer fallow was a widespread soil water conservation strategy in dryland agriculture. Actively growing plants transpire (use) a lot more water than evaporation from the soil surface alone does. Cover crops help fill the water-use void by transpiring a lot of water, helping to dry the soil surface and lower the water table before the following year. This also opens space in the soil profile for summer and fall rains to leach soluble salts from the soil surface and reduce salinity in the root zone.
Soil Erosion Control
Tillage is a popular weed control tool, but it also destroys crop residue and leaves soil exposed and vulnerable to water and wind erosion. Planting cover crops protects the soil surface from rain and wind, keeping soil firmly in place. Just because you cannot grow a cash crop on the field this year, you should not let your soil blow into the next field, letting your neighbor farm it next year.
Weed Control
An established cover crop can compete with weeds, helping suppress weed growth and weed seed production. For fields with problematic broadleaf weed histories, a cover crop mix containing only grass species is preferred. In grass cover crops, you can still use selective broadleaf weed herbicides to control the problematic broadleaf weeds of conventional or no-till systems such as Canada thistle, common ragweed, kochia, volunteer canola, and waterhemp while not killing the grass cover crop. For fields with low weed pressure, a cover crop mix containing grasses, brassicas, and legumes will provide more soil health benefits.
Soil Biological Activity
Have you heard about “fallow syndrome” before? Fallow syndrome is an induced nutrient deficiency, often seen in corn following fallow, when the population of mycorrhiza fungi is insufficient to colonize plant roots and help them acquire water and nutrients. Mycorrhizae are especially important in plant uptake of phosphorus, so plants with fallow syndrome often show phosphorus deficiency symptoms. Fallow syndrome is a major concern in corn following summer fallow or Prevented Planting without cover crop.
During the Prevented Planting year, it is important to include grass species in the cover crop mix to support and maintain the mycorrhiza population through next year. Brassica species, like radish and turnip, are often included in cover crop mixes for their deep taproot architecture and high forage value for grazing livestock, but brassicas do not support mycorrhizae. You do not want a cover crop mix consisting of brassica species alone because fallow syndrome might occur next year.
Do not forget about soil fertility and plant nutrition for cover crops. A modest application of nitrogen will help cover crop establishment, plant water use, and competition with weeds, as cover crops with adequate nitrogen will grow faster and larger than those without nitrogen. Around 46 lb/acre nitrogen (100 lb/acre urea, 46-0-0) should be enough to establish nice cover crop growth. Prevented Planting fields, being wetter than those successfully planted in spring, lost some, if not most, soil nitrogen via nitrate leaching or denitrification. Although additional nitrogen may have mineralized from soil organic matter during May and June, excess precipitation in June may have caused additional soil nitrogen loss. The best way to know is collecting 0-12 or 0-24 inch soil samples for nitrate-nitrogen analysis.
As you choose the appropriate cover crop mix on Prevented Planting fields, you must consider the pros and cons of each cover crop species and how each will help accomplish your goals. These are some helpful resources that will provide additional information on what cover crop options will work best on your fields.
Plant Analysis Sampling Guide
in Plant Analysis/by John BrekerPlant nutrient analysis is a useful management tool. The AGVISE Plant Analysis Sampling Guide discusses the importance of plant analysis in proper crop nutrition and how to collect plant
samples. It is important to collect the correct plant part at the correct plant growth stage to ensure accurate interpretation of plant analysis results. To ensure we have enough plant material to analyze in the laboratory, please collect a minimum number of whole plants or leaves per sample as instructed in the guide. To obtain the most accurate plant analysis information, follow the instructions on plant growth stage, plant part, and minimum sample size.
View the Plant Tissue Sampling Guide
High Soil Nitrogen following Drought: How to manage next year
in Drought, Nitrogen, Regional Data, Wheat/by John LeeFrom time to time, moderate to severe droughts hit the Great Plains. Such is life in semi-arid climates. When a drought occurs, it is normal to find higher residual soil nitrate-nitrogen after harvest. Since the widespread adoption of soil testing in the 1970s, we have seen this phenomenon in all major drought years: 1988, 2002, 2006, 2012, 2017 (Figure 1). The lack of precipitation and exhausted stored soil water reduces crop growth and yield, meaning much of the applied nitrogen fertilizer remains unused, showing up in the residual soil nitrate-nitrogen test. In 2017, very high residual soil nitrate-nitrogen was observed across wide geographies of western North Dakota and South Dakota (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Residual soil nitrate-nitrogen following wheat on the northern Great Plains.
Figure 2. Residual soil nitrate-nitrogen following wheat on the northern Great Plains in 2017.
Following a drought, we often get the question, “Can I count on all the soil nitrate in my soil test for next year’s crop?” The simple answer is yes; you can count on the amount of soil nitrate-nitrogen in the soil test, but you must consider additional factors. Even in drought, some parts of each field will produce higher crop yield than other parts because the better soils have higher water holding capacity (e.g. higher clay content, higher organic matter). In the high yielding zones, there is less residual soil nitrate remaining in the soil profile. Drought will create more variability in crop yield and residual soil nitrate, mostly driven by topography and soil texture.
Let’s imagine you had a wheat crop severely affected by drought, but some parts of the field still had 50% normal yield (maybe lower landscape positions, greater water holding capacity). Following harvest, the whole-field composite soil test showed 140 lb/acre nitrate-N (0-24 inch). You were skeptical about that very high residual soil nitrate level, so the crop consultant resampled the parts with better crop yield, which then had 80 lb/acre nitrate-N (0-24 inch). Using the whole-field composite soil test result of 140 lb/acre nitrate-N (0-24 inch), you would only need to apply some starter nitrogen fertilizer for next year’s crop. However, if you only applied starter nitrogen, the high yielding parts of the field with only 80 lb/acre nitrate-N (0-24 inch) would be under-fertilized, costing crop yield and profit next year, on the best soils in the field.
If you only have a whole-field composite soil test result, you must consider spatial variability in residual soil nitrate across the field. You will want to apply a base nitrogen fertilizer rate to cover the parts with lower residual soil nitrate than the field average. The base nitrogen fertilizer rate may range between 30 to 60 lb/acre N, depending on spatial variability and risk tolerance. If you do zone soil sampling, you have a much better idea of spatial variability and nitrogen fertilizer needs in all parts of your fields. Through productivity zone soil sampling, you know the residual soil nitrate level in each management zone, and you can choose different nitrogen fertilizer rates across the field.
If you only soil sample the surface soil depth (0-6 inch), you are missing 75% of the plant-available nitrate-nitrogen pie. To make good nitrogen decisions, you should collect 0-24 inch soil samples for soil nitrate-nitrogen analysis. In drought, plant roots explore deep for stored soil water and uptake whatever nitrate is found along the way. There is no way to model how much soil nitrate remains in the soil profile after drought. Following drought, the best strategy is 24-inch soil sampling and breaking fields into several management zones to determine the proper amount of nitrogen fertilizer required.