Corn Stalk Nitrate Test
To help evaluate nitrogen management in corn, you may want to try the corn stalk nitrate test as a post-mortem tool. The corn stalk nitrate test is a late-season or end-of-season plant analysis on mature corn stalks. Iowa State University developed the corn stalk sampling protocol and interpretation. If corn did not have sufficient nitrogen, the corn stalk nitrate level will be low. If corn had excess nitrogen, the corn stalk nitrate level will be high.
The corn stalk nitrate test can be useful in cropping systems with manure or corn-after-alfalfa, where a significant portion of the crop nitrogen budget comes from nitrogen mineralization. It is also helpful in more humid climates, where the residual soil nitrate-nitrogen test is not utilized. For corn silage production, it is easy to collect corn stalk samples on the go during silage harvest, making it a quick and useful tool.
Since the corn stalk nitrate test is a post-mortem tool with the goal to provide information for future years, it is not recommended in years with abnormal precipitation. In drought years, potential crop productivity is reduced, so the plant nitrogen requirement is lower than normal. In high precipitation years, soil nitrogen losses will reduce the available nitrogen supply. As a result, the corn stalk nitrate level can be very high in drought years or very low in wet years. Such results say more about environmental conditions, not the adequacy of the nitrogen fertilizer program.
When to sample
- Early: One-quarter milk line (R5 growth stage) on majority of corn kernels. Nitrate concentration may be high if collected early.
- Optimum: One to three weeks after physiological maturity (black layer, R6 growth stage) on 80% of corn kernels.
- Late: Up to harvest. Nitrate concentration may be low if rainfall has leached nitrate from plant material.
How to sample
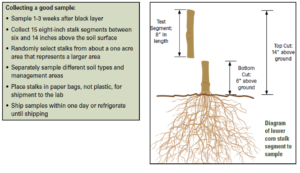
- Measure 6 inches from the ground, cut the next 8 inches of corn stalk (the 6-14 inch stalk section measured from plant base). Remove outside leaf sheath.
- Collect 12 to 15 corn stalks.
- Place corn stalks in a ventilated plant tissue bag. Do not use plastic or zipped bag.
- Do not collect diseased or damaged corn stalks.
Table 1. Corn Stalk Nitrate Test Interpretation
| Nitrate-N (NO3-N), ppm | Interpretation | Comment |
| <250 | Low | Nitrogen supply was likely deficient and limited corn grain yield |
| 250-2000 | Sufficient | |
| >2000 | High | Nitrogen supply exceeded plant requirement |